속성
모든 객체는 Object.prototype으로부터 메소드 및 속성을 상속, 모든 객체를 만들면, 해당 속성/메서드가 상속되어 있다.
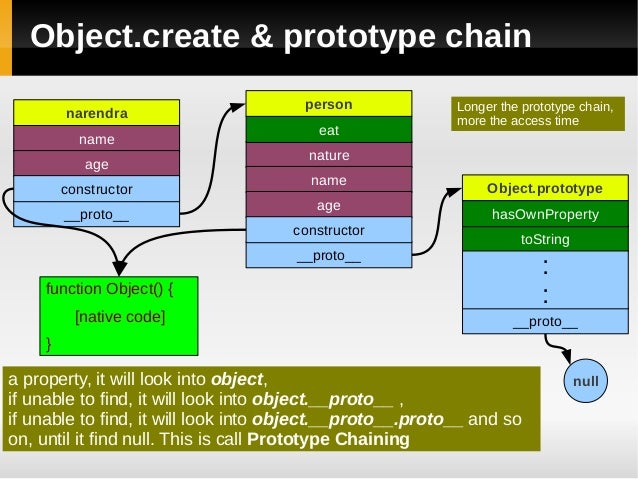
다음 코드를 보자
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 var person = { name : "child of earth" , age : 0 , nature : "cool" , eat : function ( alert(this .name + "is eating" ); } } var narendra = Object .create(person);narendra.name = "Narendra Sisdoiya" ; narendra.age = 29 ; narendra.eat(); narendra.hasOwnProperty("eat" ); narendra.hasOwnProperty("name" ); narendra.hasOwnPropery("nature" );
내장 객체인 Object와, Object.prototype이 있다.
자세한 내용은 상속과 prototype 포스팅 참조
Object.prototype.constructor
객체의 프로토타입을 생성하는 함수, 객체의 타입을 파악하는데 쓰이지만, instance of 연산자가 더 안전하다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 var o = {};o.constructor === Object ; o instanceof Object var a = [];a.constructor === Array ; var n = new Number (3 );n.constructor === Number ;
Object.prototype.__proto__
객체가 초기화될 때 프로토타입으로 사용된 객체, 즉 상속받은 내용들이 들어있다.
1 2 3 var a = {};a.__proto__ === Object ; a.__proto__ === Object .prototype;
메서드
상속받지 않은, 순수한 자신의 프로퍼티 여부를 확인한다.
1 2 3 4 5 o = new Object (); o.prop = 'exists' ; o.hasOwnProperty('prop' ); o.hasOwnProperty('toString' ); o.hasOwnProperty('hasOwnProperty' );
constructor 깨짐 없이 깔끔하게, prototype을 적용하여 객체를 생성한다. 아래와 같은 로직과 일치한다. 이때 넘겨준 객체 o는 prototype의 원리와 같이 객체를 공유하게 된다.
1 2 3 4 5 function object (o ) function F ( F.prototype = o; return new F(); }
Object.create(프로토타입이 될 객체, 추가할 프로퍼티 객체)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 var person = { name : "hi" , friends : ["hi" , "ho" ] }var p1 = Object .create(person);var p2 = Object .create(person);var p3 = Object .create(person, { name : { value : "Gre" } })
생성자 함수를 만들어 create를 사용할 경우
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 function Shape ( this .x = 0 ; this .y = 0 ; } Shape.prototype.move = function (x, y ) this .x += x; this .y += y; console .info('Shape moved.' ); }; function Rectangle ( Shape.call(this ); } Rectangle.prototype = Object .create(Shape.prototype); Rectangle.prototype.constructor = Rectangle; var rect = new Rectangle();console .log('Is rect an instance of Rectangle?' , rect instanceof Rectangle); console .log('Is rect an instance of Shape?' , rect instanceof Shape); rect.move(1 , 1 );
Object.create(Shape.prototype) : create의 인자로 프로토타입으로 쓰일 객체를 넘겨줘야 한다.Shape.call(this) : 상속 포스팅에도 설명했듯이, Shape의 this인자들을 Rectangle 컨텍스트에서 생성하게 하여 자신의 프로퍼티를 가지게 된다.
Object.defineProperties()
데이터 프로퍼티와, 접근자 프로퍼티 를 셋팅한다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 var obj = {};Object .defineProperties(obj, { '_x' : { value: 0 , writable: true }, 'x' : { get : function() { return this ._x; }, set : function(newValue) { this ._x = newValue+1 ; } }, '_y' : { ... } });
configurable, enumerable 와 같은 속성을 설정하지 않으면 default로 false가 할당된다.
언제 사용할까?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Object .prototype.imFunc = function ( console .log('aa' ); } var a = new Object ();for (var b in a) { console .log(b); }
for in문에서 순회하고 싶지 않아도, 함수가 나온다. 이때 사용해보자
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Object .defineProperty(Object .prototype, 'imFunc' , { enumerable: false , configurable: false , writable: false , value: function ( console .log('aa' ); } }); for (var b in a) { console .log(b); }
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor()
접근자/데이터 프로퍼티 객체를 읽어온다.
1 2 3 4 5 var descriptor = Object .getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, "_x" );alert(descriptor.value); alert(descriptor.configurable); alert(descriptor.get);
Object.preventExtensions(), Object.isExtensible()
새로운 프로퍼티를 추가할 수 없도록한다. 값 수정은 가능.
Object.seal(), Object.isSealed()
새로운 프로퍼티를 추가할 수 없도록한다. 값 수정은 가능하지만, configurable 값은 false로 바꾼다.
Object.getOwnPropertyNames()
파라미터 : object
리턴 : 문자열 배열
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 var arr = ['a' , 'b' , 'c' ];console .log(Object .getOwnPropertyNames(arr).sort()); var obj = { 0 : 'a' , 1 : 'b' , 2 : 'c' };console .log(Object .getOwnPropertyNames(obj).sort());
prototype을 리턴한다.
1 2 3 4 Object .getPrototypeOf('foo' );Object .getPrototypeOf('foo' );
ES6
Object 병합하기
파라미터 : 타겟, 소스
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 var o1 = { a : 1 };var o2 = { a : 1 , b : 2 };var o3 = { c : 3 };var obj = Object .assign(o1, o2, o3);console .log(obj); console .log(o1);
객체를 읽기전용으로 바꾼다. 프로퍼티 추가/삭제/변경, 이나 enumerability, configyrability 등의 속성 변경 또한 막는다.
ES8
열거 가능한 객체를 [key, value] 배열로 만들어 리턴함
파라미터 : key, value 쌍의 객체
리턴 : key, value 쌍의 배열
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 var obj = { foo : 'bar' , baz : 42 };console .log(Object .entries(obj));var obj = {a : 5 , b : 7 , c : 9 };for (var [key, value] of Object .entries(obj)) { console .log(key + ' ' + value); } Object .entries(obj).forEach(([key, value] ) => { console .log(key + ' ' + value); });
Reference https://medium.com/@bluesh55/javascript-prototype-이해하기-f8e67c286b67
http://unikys.tistory.com/320
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Object/